Security Terms & Definitions
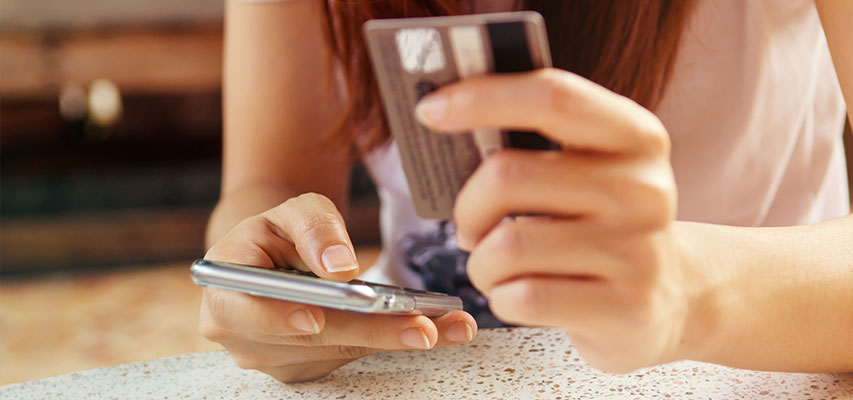
Account Fraud: Encompasses various types such as checking account fraud, credit card fraud, ATM fraud, and identity theft. Protect your personal information, never respond to unsolicited requests, and only provide information on secure websites. Avoid sending credit card details via email, report lost or stolen payment methods immediately, review your statements regularly, and contact Connex immediately if you suspect fraud.
Adware: Software that delivers advertising while in use, typically to offset development costs. Often confused with spyware or malware, which can be harmful.
Anti-virus Software: Detects, repairs, and removes virus-infected files and may also target spyware, malware, Trojans, and other malicious programs. Must be updated regularly to remain effective. Examples: AVG, Avast.
Firewall: A software or hardware system that limits unauthorized access to networks or computers. Affordable personal firewalls are available for both home and business use.
Keylogger: A program that records keystrokes and can capture passwords, chats, and screenshots, often installed unknowingly through malicious links. Poses a serious privacy risk.
Malware: Malicious software intended to cause harm, steal data, or attack other systems. Can be installed by clicking pop-ups or visiting harmful websites.
Pharming: A phishing variant that redirects users to fraudulent websites without their knowledge, often via malicious code on a computer or server.
Phishing: A scam to capture sensitive information by imitating legitimate sources, often through deceptive emails or calls.
Ransomware: Malware that encrypts data and demands payment for decryption. Spreads through email attachments, infected programs, or compromised websites.
Shoulder Surfing: Observing someone entering sensitive information, such as a PIN or password.
Social Engineering: Manipulating people into revealing confidential information, often exploiting human trust.
Spam: Unsolicited, often commercial, email sent in bulk. Typically filtered by anti-spam software.
Spyware: Software that secretly monitors activity, capturing sensitive information and possibly delivering ads without consent. Examples of free removal tools: AVG, Avast, Malwarebytes.
Trojan Horse: Malicious software disguised as legitimate programs, often hiding in downloads or email attachments.
Vishing: Voice phishing using phone calls or automated systems to trick individuals into giving personal information.
Worms: Self-replicating programs that spread through networks, often disrupting systems.
Connex will never call you and ask for PINs, passcodes, or account numbers. If you receive a suspicious call or text, hang up and call us directly at 1-800-CR-UNION (203-603-5700).
© 2026 Connex Credit Union.